Explore the expanding world of decentralized blockchain-powered DApps from NFT DApps: decentralized applications empowering digital ownership and creative monetization.
NFTs and DApps work hand-in-hand to form an exciting ecosystem where digital ownership, decentralized finance, and programmable assets converge, providing innovative solutions across various industries.
NFTs and DApps: Two Intersecting Technologies
Decentralized applications (DApps) and nonfungible tokens (NFTs) are key elements of blockchain and cryptocurrency ecosystems, each serving distinct but complementary purposes. Even though their functions often conflict, there have been instances in which their roles overlap to enhance one another.
NFTs can be employed in DApps to represent ownership or access privileges for both physical and virtual assets, tokenizing unique goods like in-game assets, digital art, or real estate through ERC-721 or ERC-1155 standards.
NFTs are widely utilized as virtual assets in gaming DApps. Since these assets can be bought or traded on secondary markets, this increases ownership legitimacy across many virtual worlds or games.
NFTs have made digital asset creation, management, and trading increasingly attractive through DApps dedicated to tokenized creations by content creators and artists alike. Tokenizing allows artists and content producers to produce one-of-a-kind digital assets that consumers can buy or own safely, providing creators with new ways of engaging directly with their audiences while giving collectors access to an easily verifiable method of digital asset ownership.
Smart contracts strengthen the convergence between DApps and NFTs through their programmability. DApps can use smart contracts to automate various NFT tasks related to content licensing, royalty distribution, and dynamic features within an NFT itself; such an increase in programmability further expands their usefulness and functionality.
What Are NFT DApps?
NFT DApps are blockchain-based applications that incorporate nonfungible tokens. Users of such apps can use NFT DApps to create, buy, sell, and trade original digital products like artwork, collectibles, and in-game items using nonfungible tokens backed by blockchain technology – offering gamers, artists, and content creators more ownership options with greater transparency and security than ever before!
NFT DApps serve an invaluable function by creating a decentralized marketplace, encouraging peer-to-peer transactions, offering innovative ownership forms, disrupting established sectors, and opening access to the global digital economy.
Types of NFT DApps
NFT DApps cover an expansive spectrum, each designed for specific digital and blockchain technology areas.
Collectibles Art platforms
Artists tokenize their works as non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on platforms such as OpenSea and Rarible that act as marketplaces to buy, sell, and exchange original digital assets. At the forefront of an emerging digital art scene, these platforms help artists assert ownership and value within the blockchain ecosystem.
Gaming & Virtual worlds
In the gaming and virtual worlds, DApps like Decentraland and CryptoKitties use NFTs to represent in-game assets such as characters or items, creating a vibrant virtual economy. Thanks to blockchain technology’s convergence with gaming, this has resulted in innovative concepts like play-to-earn that allow users to earn money while engaging with blockchain-based games in virtual worlds.
Virtual Real Estate
Platforms offering virtual real estate give NFTs an intriguing edge. Users not only develop and make money off their virtual properties but can also buy, sell, and trade them – giving rise to interest in user-owned decentralized virtual worlds and an entirely new generation of digital property rights.
Marketplaces
Marketplaces like Foundation and Mintable are key components of the NFT ecosystem, providing artists and producers with the tools they need to sell their NFTs to an international audience. These platforms act as intermediaries between creators and fans while expanding the industry as a whole.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and NFT Collateral
Not only have NFTs become creative currency, but they have also found applications in DeFi. DApps like Aavegotchi and Rarible employ NFTs as collateral within DeFi protocols, allowing users to lend or borrow based on the value of their NFT holdings and opening up new possibilities at the intersection between digital ownership and decentralized finance.
Steps for Launching an NFT DApp
Developing and launching an NFT DApp involves several steps, as outlined below:
Concept Defining
Before undertaking the development of an NFT DApp, it is vital that a team clearly defines its concept. This involves outlining goals, user demographics, and any distinctive qualities that will set their product apart in an already saturated NFT market.
Select a Blockchain
When developing an NFT DApp, selecting an appropriate blockchain platform is paramount. Ethereum stands out as an attractive option thanks to its solid infrastructure and broad support of NFT standards such as ERC-721 and ERC-1155; alternatively, other blockchains like BNB Smart Chain may be considered depending on individual project requirements.
Set up environment for development
Install the necessary dependencies and tools for development. Create your own development environment. This may include smart contract development kits, blockchain development frameworks, or additional testing or scripting tools as needed.
Smart contracts
Create Smart Contracts Develop smart contracts to regulate NFTs’ creation, ownership, and distribution. These agreements include terms for minting, purchasing, selling, and transferring an NFT, as well as their features and characteristics.
Wallet Intergration
Integrate wallets so users can safely handle NFTs. Integration may also be required to enable engagement between cryptocurrency wallets like MetaMask or Trust Wallet and your DApp.
Minting functionality
Create minting functionality so creators and artists can tokenize their assets with NFTs. Developers must design an intuitive user interface (UI), so creators and artists can easily upload work, add metadata, and mint NFTs on the blockchain for a user-friendly platform navigation experience.
If applicable, implement features for buying, selling, and trading NFTs within your marketplace DApp, such as auctioning bidding and real-time pricing adjustments.
Users should be able to effortlessly explore, purchase, and sell NFTs with an engaging UI that makes browsing, buying, and selling simple. Consider including features like filters and search and an easy wallet interface.
Testing
Before deploying the NFT DApp onto the blockchain, ensure it has been thoroughly tested to discover any flaws or vulnerabilities and address them before uploading all related files and smart contracts onto it. Doing this ensures global user accessibility of the NFT DApp.
Launch and Marketing
A strategic approach should be employed when introducing an NFT DApp into the market to generate interest and ensure its successful launch. Begin by releasing smart contracts onto the mainnet to officially kick off your NFT DApp, and devise a comprehensive marketing plan concurrently to expand exposure.
Create an engaging narrative about the unique value proposition of your NFT DApp and share it across various platforms, such as forums, social media sites, and cryptocurrency communities. Connect with influential figures and thought leaders within this sector to broaden your audience and build credibility in the NFT industry.
Establish a website that serves as an information hub and includes guidelines and user-friendly interfaces to assist newcomers with understanding the platform. At the launch stage, it is crucial to implement an efficient community feedback loop to quickly resolve user complaints while encouraging an inviting community climate.
After launch, teams must establish an open dialogue with users, address their issues promptly, and adjust the DApp in response to changing market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does dApp stand for?
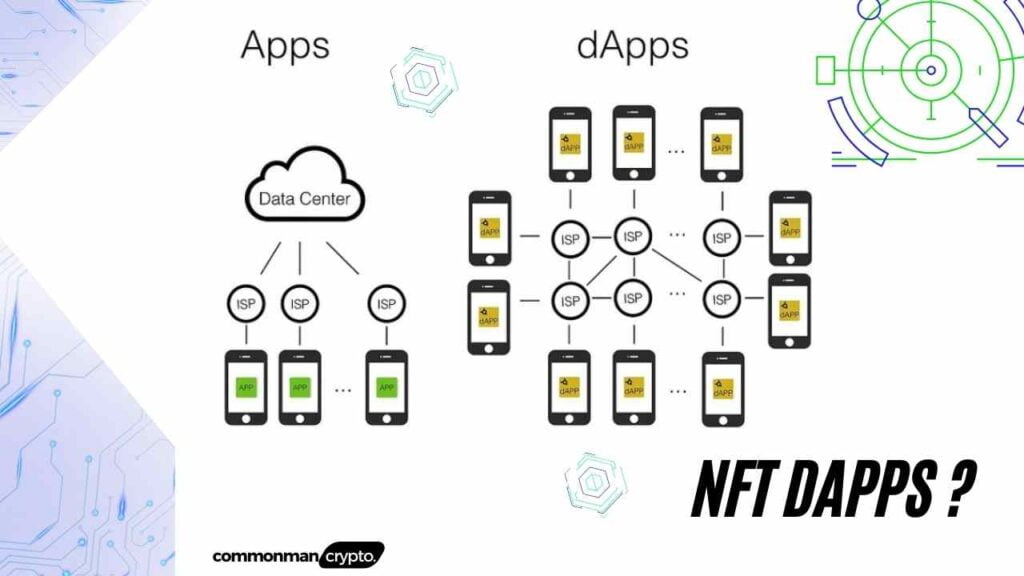
Decentralized applications (dApps or “dapps”) are digital apps that run across a network of computers rather than on one single machine, known as blockchain technology.
What is an example of a dApps?
BitTorrent, Popcorn Time, and Tor are examples of decentralized apps running on P2P networks that fall under this classification; with blockchain technology’s rise came to their resurgence – including cryptocurrency such as Bitcoin – being one such example of decentralized applications (dApps).
What does NFT mean?
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs), often referred to as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), are blockchain-based tokens that represent unique assets like art pieces, digital content, or media files. Each NFT can be seen as an irrevocable digital certificate of ownership and authenticity for each asset- physical or digital.
What are DApps used for?
A decentralized application (DApp) is an open-source, distributed software program that runs on a P2P blockchain network rather than one computer. DApps function like any other website or mobile application but are P2P-supported instead.
Are DApps the future?
DApps are emerging as digital fortifications for future interactions on the internet, providing transparency, security, and data integrity in interactions across digital spaces. DApps promise unrivaled power while simultaneously offering protection and inclusion to users worldwide.
Obstacles to Creating and Launching an NFT DApp
Launching and developing an NFT DApp presents many obstacles, with technical scalability being one of the main hurdles due to increasing NFT transaction demand and complexity. Ensuring an ideal user experience becomes imperative, necessitating creative solutions to manage network congestion or slow transaction processing times.
Smart contract security is of utmost importance, as any vulnerabilities could have severe repercussions for users and the integrity of NFTs. Furthermore, competing against other Dapps for users’ attention can make standing out even harder.
Complexities associated with legal ambiguities arise regarding intellectual property rights and regulatory compliance issues. To overcome such challenges, an effective combination of technological knowledge, security protocols, user-centric design techniques, and an acute understanding of NFT regulatory environments must be utilized.